Engineered timber buildings are becoming increasingly popular
In many countries, construction is a way to accelerate the economic recovery from the pandemic but it’s also a major source of carbon emissions. One way to bridge this issue is to increase the construction of more sustainable buildings.
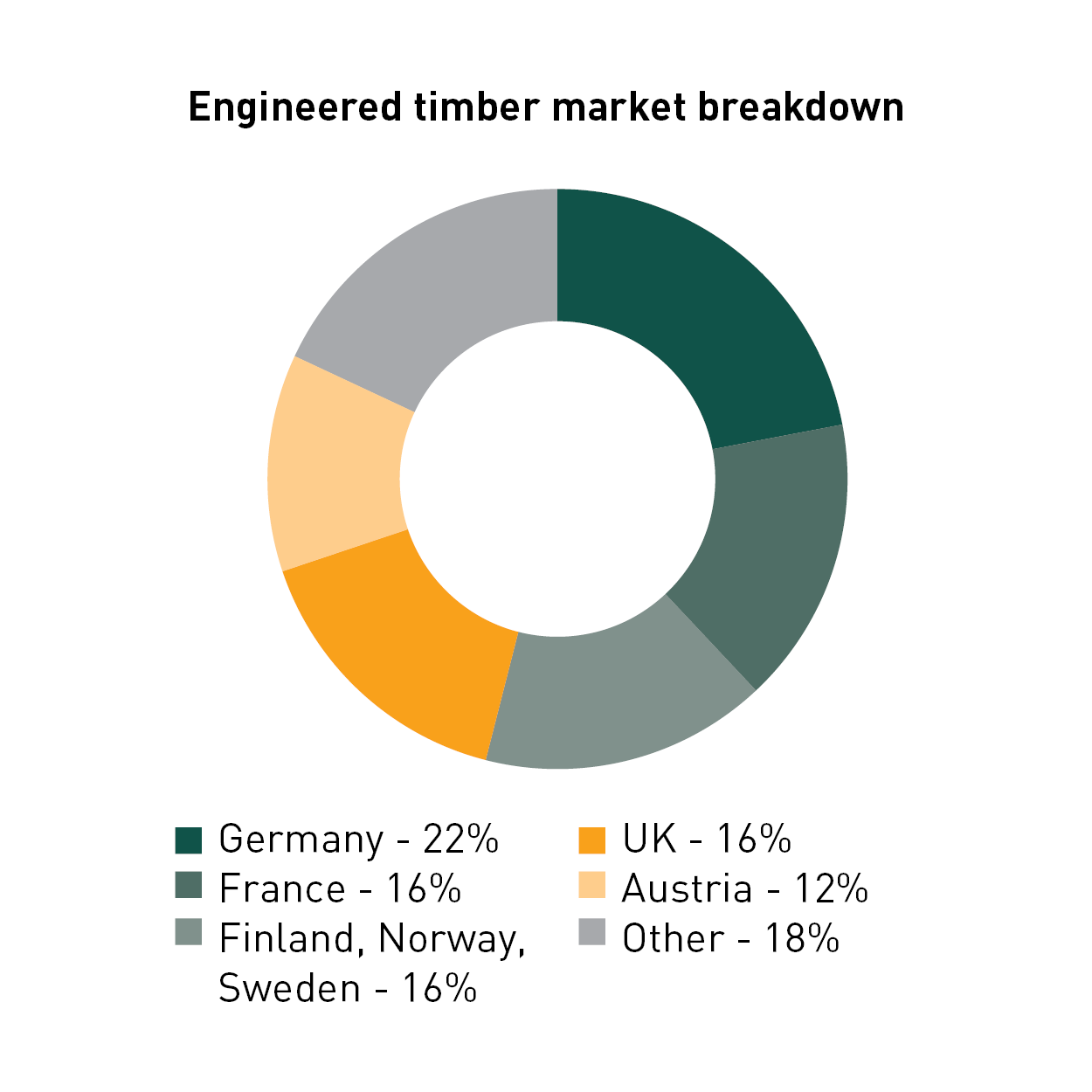
Engineered timber buildings tick this box, and a combination of technological innovation, greater sustainability and reduced costs has seen the number of such developments increase globally.
Construction using concrete and steel is highly carbon-intensive, compared to trees which capture and store carbon dioxide as they grow, making timber a far greater climate-friendly building material. Timber construction also uses materials derived solely from managed fast growth plantations meaning construction is sustainable and does not rely on harvesting old-growth forests.
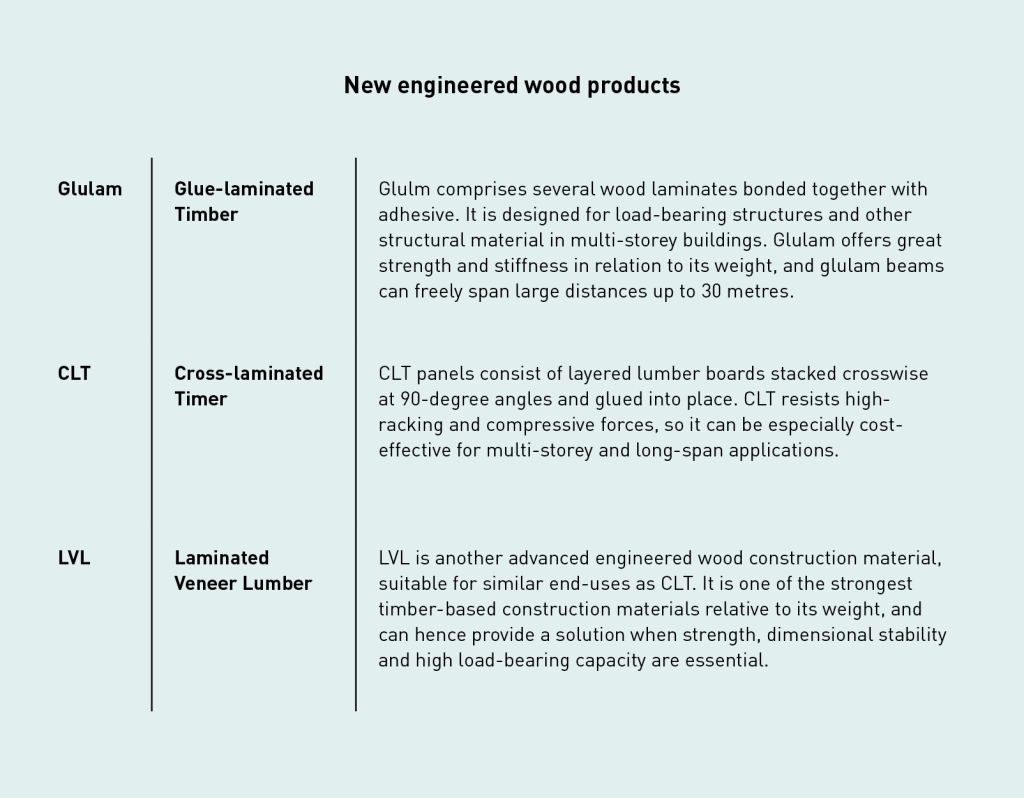
The rapid development in the market has been made possible by the technological breakthroughs of new engineered wood products, such as Glue-laminated Timber (Glulam), Cross-laminated Timber (CLT), and Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL).